Configuring sizing and scaling for Azure container instances
Azure container instances cannot be resized after deployment; you will notice there are no options to do so in the Azure portal. The only way to resize a container instance is to redeploy the solution with the required size. If you are looking to scale horizontally (multiple instances), you can achieve this through the container group or by deploying several instances. To configure sizing for your container instance, you will recall that on the instance setup, there is a Change size sizing option, as illustrated in the following screenshot:

Figure 11.40 – ACI: Size
The following screen will pop up for you to configure the desired size for your container instance:
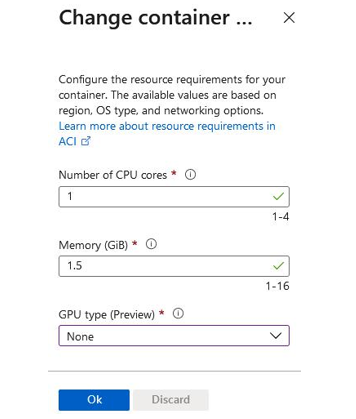
Figure 11.41 – ACI: Size options
For Number of CPU cores, you can select a value between 1 and 4. You can select from between 1 and 16 for Memory (GiB). Where you have GPU-based applications or requirements, you will note that you can change your GPU type. Note that GPUs are only available to some regions, and at the time of writing, this is still a preview feature. The options available are K80, P100, or V100. The GPU selected enables further options for selecting the number of GPUs you would like, 1, 2, or 4, as shown in the following screenshot:
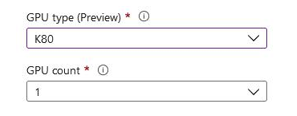
Figure 11.42 – ACI: GPU options
Top Tip
1 gibibyte (GiB) = 1,024 mebibyte (MiB) where GB = 1,000 megabytes (MB). Most people refer to MB or GB, and due to easy conversions and the internet industry, the conversion is often defined as 1,000 MB in 1 GB, where computers work on a binary-based number system, meaning that all numbers are calculated from a base of 2. Therefore, GiB is defined as 2^10 MiB, which is 1,024.
You now know about the sizing available to container instances, so in the next section, we will explore how Kubernetes can assist in the management of our containers.
